Blotchy Swollen Red Rash Face and Body Baby Fever
Skin rashes in children
Childhood rashes are mutual. Most rashes are harmless and disappear without the need for handling. See your GP or call GP out of hours service if your child has a rash and seems unwell, or if you're worried.
About pare rashes in children
It'south especially important to be aware of the symptoms of meningitis, see section below.
Also beneath is information on some of the virtually common rashes in children.
This guide may give you a better idea of the cause of the rash. Merely don't rely on information technology to diagnose your baby's condition if they show any signs of beingness unwell. E'er see a GP or contact a GP out of hours service for a proper diagnosis.
- read near causes of skin rashes in babies
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an infection of the deeper layers of skin and underlying tissue.
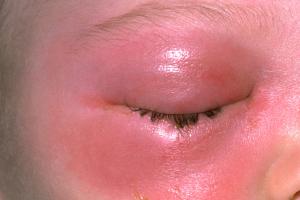
About cellulitis
- the afflicted area will exist scarlet, painful, swollen and hot
- it oftentimes affects the legs, but can occur anywhere on the body
- your kid will probably also have a fever
Contact your GP or GP out of hours service if an area of your child'due south skin turns red, hot and tender. Do this immediately if your child appears unwell. Cellulitis commonly responds well to treatment with antibiotics.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a viral affliction that most children catch at some betoken. It nearly commonly affects children under 10 years of age.
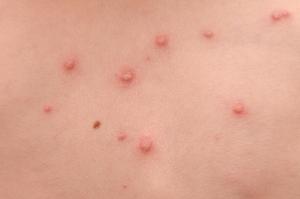
Nearly chickenpox
- it causes a rash of itchy spots that turns into fluid-filled blisters
- they crust over to form scabs, which later a while drop off
- some children only accept a few spots, others have them over their entire torso
- the spots are near likely to appear on the face, ears and scalp, under the arms, on the chest and belly, and on the artillery and legs
There'due south no specific treatment for chickenpox. You tin take steps to relieve the symptoms. For example, paracetamol can assist relieve fever (don't give aspirin to children under 16). Calamine lotion and cooling gels can be used to ease itching.
Eczema
Eczema is a long-term condition that causes the skin to become itchy, ruby-red, dry and croaky. The most common type is atopic eczema, which mainly affects children but can go on into adulthood.
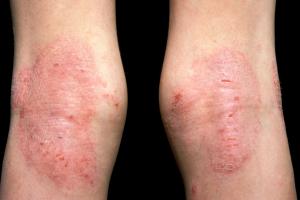
About atopic eczema
- commonly develops behind the knees or on the elbows, neck, eyes and ears
- it isn't a serious condition, simply if your child later becomes infected with the herpes simplex virus, it can cause the eczema to flare upwards into an outbreak of tiny blisters and volition cause a fever
Erythema multiforme
Erythema multiforme is a skin rash (usually mild). Information technology is caused by an allergic reaction to the herpes simplex virus.
About Erythema multiforme
- the spots look like targets, with a dark ruddy heart and paler ring around the exterior
- the hands or feet tend to be affected outset, followed past the limbs, upper body and face
- your child will probably feel unwell and may have a fever, which yous should be able to treat with over-the-counter medicine
- it may take from two to vi weeks before they feel meliorate
See your GP if your child has a rash and seems unwell.
In rare cases, erythema multiforme can be triggered by a reaction to certain medications, such as an antibiotic or anticonvulsant.
This more than severe form is called Stevens-Johnson syndrome and it tin be life-threatening.
Paw, human foot and mouth disease
Manus, foot and rima oris disease is a common, contagious infection.
Nigh hand, foot and mouth illness
- causes mouth ulcers and spots and blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- it's most mutual in young children (particularly those under x), but it can also affect older children and adults
In that location's no cure for hand, pes and mouth disease. It'south easily spread, then you should keep your kid abroad from school or nursery until they're better.
Your child's immune arrangement will fight the virus. It should articulate upward afterward about seven to 10 days.
Make certain your child drinks enough of fluid. If eating and swallowing is uncomfortable for them, give them soft foods, such equally mashed potatoes, yoghurt and soup.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a common and highly contagious skin infection that causes sores and blisters. It is caused by bacterial infection. It isn't usually serious and often improves within a week of treatment.
There are two types of impetigo – bullous and not-bullous.
About bullous impetigo
- typically affects the torso (the surface area of the body betwixt the waist and neck)
- causes fluid-filled blisters that burst after a few days to get out a xanthous crust
About non-bullous impetigo
- typically affects the skin around the nose and mouth
- causes sores that apace flare-up to go out a yellow-brownish crust
Run across your GP if you recall your child has impetigo. If it is impetigo, antibiotics volition usually be prescribed. This is an effective handling, clearing up the infection.
Keratosis pilaris ('chicken pare')
Keratosis pilaris is a mutual and harmless pare condition.
Nearly keratosis pilaris
- the skin on the back of the upper arms becomes crude and bumpy, equally if covered in permanent goose pimples
- sometimes, the buttocks, thighs, forearms and upper dorsum can also be afflicted
- typically begins in childhood and gets worse during puberty
- some people find it improves after this and may even disappear in adulthood
In that location'south no cure for keratosis pilaris. It often gets better on its own without treatment. There are some measures you can have that may improve your child'south rash. These include using non-soap cleansers rather than soap, and an emollient to moisturise their peel.
Your GP or pharmacist will be able to recommend a suitable cream.
Measles
Measles is a highly infectious viral disease that almost commonly affects young children. It's now uncommon in Northern Ireland because of the effectiveness of the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccination programme, with high levels of vaccination.
Virtually measles
- the measles rash is cherry-brown blotches
- it ordinarily starts on the confront, head or upper neck and so spreads outwards to the rest of the body
- your child may as well have a fever and cold-like symptoms
Call your GP surgery if you think your child has measles. It's all-time to phone before visiting. This is because the surgery may demand to make arrangements to reduce the gamble of spreading the infection to others.
Measles ordinarily passes in about seven to x days without causing farther problems. Paracetamol or ibuprofen can be used to relieve fever, aches and pains (don't give aspirin to children under 16).
Also, make sure your child drinks plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection.
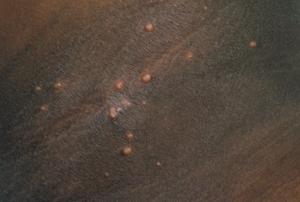
Nearly molluscum contagiosum
- causes clusters of pocket-sized, firm, raised spots to develop on the peel
- commonly affects young children aged one to five years, who tend to take hold of it subsequently shut physical contact with another infected child
- is normally painless, although some children may experience some itchiness
- usually goes away within 18 months without the need for handling
Molluscum contagiosum is highly infectious. Nearly adults are resistant to the virus. This means they're unlikely to catch it if they come into contact with it.
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea is quite a mutual skin condition.
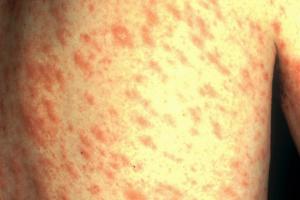
About pityriasis rosea
- causes a temporary rash of raised, cerise scaly patches to develop on the body
- most cases occur in older children and young adults (aged between ten and 35)
- the rash can be very itchy
- in nigh cases, it clears upwardly without treatment in two to 12 weeks
- in rare cases it can last up to five months
Emollients, steroid creams and antihistamines can be used to aid salve the itchiness. The rash doesn't usually leave scars. The skin can sometimes be discoloured afterwards.
Prickly oestrus (oestrus rash)
Prickly heat (heat rash) is also known as miliaria.
Nearly prickly heat (heat rash)
- it is an itchy rash of modest, raised crimson spots that causes a stinging or prickly awareness on the skin
- information technology occurs when the sweat ducts in the outer layer of skin (epidermis) are obstructed
- you can become a rut rash anywhere on your torso, only the face, neck, dorsum, chest or thighs are most often afflicted
- infants can sometimes get a prickly heat rash if they sweat more than than usual – for example, when it's hot and humid or if they're overdressed
Information technology isn't a serious condition and rarely requires whatever specific handling.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting (chronic) peel condition.
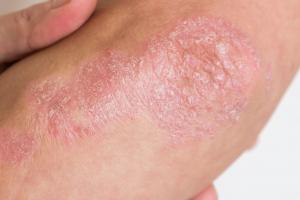
Nearly psoriasis
- that causes red, flaky, crusty patches of skin covered with silvery scales
- the severity of psoriasis varies greatly from person to person- for some people, information technology's just a minor irritation, but for others it can have a major touch on their quality of life
There's no cure for psoriasis. At that place are a number of treatments, available through your GP, which can assistance improve the symptoms and appearance of skin patches. For case, topical corticosteroids are creams and ointments that can be practical to the skin.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a highly infectious fungal skin infection.
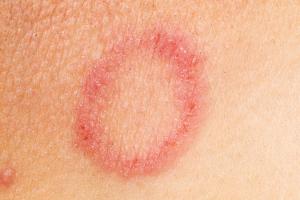
About ringworm
- causes a ring-like cerise or silver patch on the skin that can exist scaly, inflamed or itchy
- often affects the artillery and legs, but information technology can appear almost anywhere on the trunk
Other similar fungal infections tin can affect the scalp, feet, groin and nails.
Ringworm tin can usually exist hands treated with antifungal medicines. These are available from a chemist's shop. Enquire your pharmacist if you need advice about treatment.
Ringworm of the scalp can cause scaling and patches of hair loss.
Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin status that's intensely itchy.
About scabies
- it'due south caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin
- in children, scabies is unremarkably spread through long periods of pare-to-skin contact with an infected adult or child – for example, during play fighting or hugging
- the mites like warm places, such as skin folds, between the fingers, under fingernails, or effectually the buttock creases
- the mites leave pocket-size red blotches, which are oft found on the palms of the easily or soles of the feet
- in infants, blisters are unremarkably found on the soles of the feet
See your GP if you think your child has scabies. It's not usually a serious status, but it does demand to be treated. Your GP volition prescribe a balm or foam.
Cerise fever
Cerise fever is a highly contagious bacterial infection.
About scarlet fever
- usually affects children betwixt ii and eight years of age
- causes a distinctive pink-cerise rash, which feels like sandpaper to touch and may be itchy
- often starts with a sore throat, fever and headache, with the rash developing two to 5 days after infection
- the rash usually occurs on the chest and breadbasket before spreading to other areas of the trunk, such as the ears and neck
- sometimes a white coating may class on the natural language, which peels abroad afterward a few days, leaving the tongue red and bloated - this is known equally a 'strawberry tongue'
Red fever usually clears upwardly after about a week. But see your GP if y'all think your kid may have it. Your GP will prescribe an antibiotic to care for it.
Slapped cheek syndrome
Slapped cheek syndrome is a viral infection that's mutual in children aged six to 10.
About slapped cheek syndrome
- causes a distinctive bright red rash to develop on both cheeks
- this can look alarming, but it usually clears up past itself in one to three weeks
Unless your child is feeling unwell, they don't need to stay away from school.
Once the rash appears, the infection is no longer contagious. It's a good thought to permit your child'southward school know about the infection.
Urticaria (hives)
Urticaria is also known as hives, weals, welts or nettle rash.
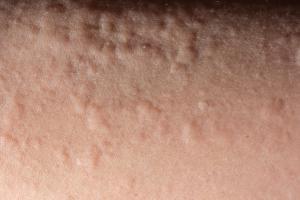
About hives
- is a raised, itchy rash that can touch one part of the body or exist spread across large areas
- information technology's a common peel reaction that oft affects children
- occurs when a trigger causes high levels of histamine and other chemical messengers to be released in the peel
- these substances cause the claret vessels in the peel to open up upward, resulting in redness or pinkness, and swelling and itchiness
At that place are many possible triggers of urticaria, including allergens, such equally food or latex, irritants, such as nettles, medicines, and physical factors, such as oestrus or do. Sometimes, a crusade can't be identified.
The rash is commonly short-lived and mild. It can ofttimes be controlled with antihistamines. Inquire your pharmacist for advice. Urticaria tin can be one of the first symptoms of a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Call 999 immediately and ask for an ambulance if y'all or someone else is experiencing anaphylaxis.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord (meninges).
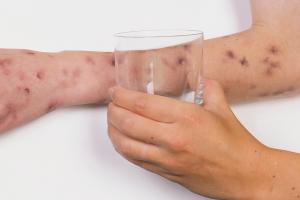
Nearly meningitis
- the archetype rash associated with meningitis usually looks like small, ruby pinpricks at first
- it and then apace spreads over the body and turns into red or majestic blotches that won't fade when a drinking glass is rolled over it (this won't e'er develop)
Meningitis can be serious if not treated rapidly. Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest emergency department if you retrieve you or your kid might be seriously sick.
More useful links
- How to utilize your health services
The information on this page has been adapted from original content from the NHS website.
For further information come across terms and conditions.
whittleseliestionce.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.nidirect.gov.uk/conditions/skin-rashes-children
0 Response to "Blotchy Swollen Red Rash Face and Body Baby Fever"
Postar um comentário